introduction RFID technology has the following characteristics: data read and write function; label is easy to be miniaturized and diversified; environmental resistance; reusable; strong penetrability; data memory capacity is large, compared with traditional barcodes, barcode recognition items Kind, while RFID technology identifies each individual object object. Since the application of RFID involves many industries, its related standards are intertwined and very complicated. From the category, RFID standards can be divided into the following four categories: technical standards (such as RFID technology, IC card standards, etc.); data content and coding standards (such as coding formats, grammar standards, etc.); performance and conformance standards (such as test specifications) Etc); application standards (such as shipping labels, product packaging standards, etc.). 6 Big Holes Helmets,Helmets For Skateboard,Skating Helmet,Helmets Online Store YONGKANG YISHANG INDUSTRY&TRADE CO.,LTD. , http://www.yes-trade.com
The basic concept of the Internet of Things is to connect and connect any item with the Internet through information sensing equipment, and exchange information and communicate to realize intelligent identification, location, tracking, monitoring and management. The perceptual extension layer is the most extensive layer in the entire IoT architecture. The smart card belongs to the perceptual extension layer in the entire IoT architecture.
The competition in the traditional smart card market has already narrowed the survival space of enterprises. In recent years, the rise of the Internet of Things has brought a very good opportunity for the smart card to be revived. As a carrier that perceives the physical world, stores information and transmits data, with the development of the Internet of Things industry, the application and development of smart cards is getting faster and faster, and it is more widely used in finance, logistics, home and food traceability. .
Smart card technology analysis
A smart card is a plastic card with embedded chips. According to different types, these cards can store data, process data, and be read and written. Smart cards can be divided into contact cards and contactless cards. Class, where:
Contact card
Contact cards require a card reader for reading and writing information. Unlike a tape on a credit card, the card is embedded with a small piece of metal on the surface. When the card is inserted into the card reader, the small piece of metal is in contact with an electronic connector, and the chip is read through the electronic connector. Write data. From the structure of the card, contact cards are mainly divided into the following two types of cards:
Ø Memory Card: The memory card does not contain complex processors, it cannot manage files dynamically. The communication between the memory card and the card reader is synchronous communication. The IC card in the IC phone is a memory card.
Ø Microprocessor card: The microprocessor card is the main discussion here. The biggest difference between her and the memory card is that she has the ability to process data dynamically. The system structure of the microprocessor card is somewhat like a PC. She also has ROM, RAM, CPU and EEPROM.
2, contactless card
The contactless smart card looks very similar to a normal plastic credit card. It has an antenna and a microelectronic chip embedded in the card body. When it is placed close to the reader's antenna, a message can be completed between them. exchange. This allows it to exchange information with the coupling sensor without any contact, and the processing time is extremely short. This feature makes the contactless smart card in places that require large quantities of ultra-fast operation like highway toll stations. Become the ideal solution.
Currently, smart cards widely used in IoT applications are mainly microprocessor cards (SIM cards, bank cards, etc. are microprocessor cards) and non-contact cards, especially RFID, user identification cards, and near-field payment SIM cards. And JAVA card, etc., the following analysis and comparison of these card principles and performance.
2.1 RFID
The basic working principle of RFID is to use space inductance coupling or electrical coupling to communicate, in order to achieve the purpose of automatically identifying the identified object. Mounting the RFID tag on the identified object (paste, insertion, hang, implant, etc.), when the marked object enters the reading range of the radio frequency identification system, the contactless information communication between the tag and the reader The tag sends the carrying information to the reader, and the reader receives the information and decodes it, and transmits it to the background processing computer to complete the entire information processing process. 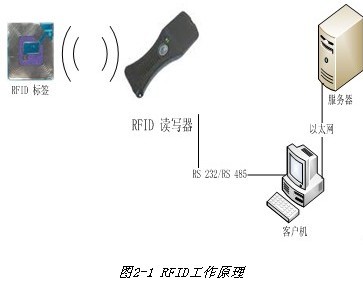
The working frequency band of the RFID system can be low frequency (LF) (30-300 kHz, typical frequency is 125 kHz, 134.2 kHz), high frequency (HF) (3-30 MHz, typical frequency is 13.56 M Hz), ultra high frequency (UHF) Four frequency bands (300-968MHz, typical frequency 869.6MHz, 915.3MHz), microwave (MW) (2.45-5.8GHz, typical frequency is 2.45GHz), the specific frequency is determined by the radio management department of each country or region. According to different working frequency bands, in the case of passive, its technical characteristics and application range are also different, as shown in the following table: 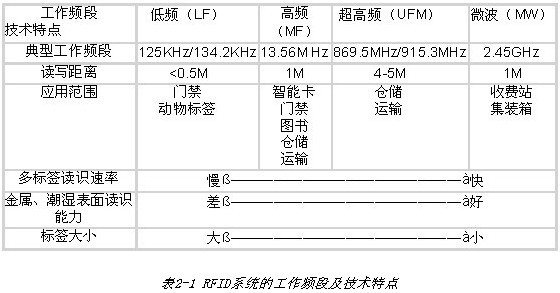
Specifically, RFID-related standards cover electrical characteristics, communication frequencies, data formats and metadata, communication protocols, security, testing, applications, and more.
The international standardization bodies related to RFID technology and applications are: International Organization for Standardization (ISO), International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), International Telecommunications Union (ITU), World Union Postal (UPU). In addition, other regional standardization bodies (such as EPC global, UID Center, CEN), national standardization bodies (such as BSI, ANSI, DIN) and industry alliances (such as ATA, AIAG, EIA) also develop RFID-related areas. , national, or industry alliance standards, and promoted to international standards through different channels.
2.2 User Identification Card
SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) The most basic characteristics of the user identification module, one is to do identity and the other is to do security services. The identity is the authentication of the network, and it can also do a lot of application data authentication. From the perspective of security services, it can store some information securely, or more confidential information can be stored in the SIM card. At the same time, the SIM card has its own authentication and resolution capabilities.
The SIM card for the sensor terminal requires a longer data retention time. The average SIM card storage time in the mobile phone is about 10 years, and it takes longer to maintain in industrial or special industries, ten years, fifteen years or even higher. In addition, there are times of erasing. The cards used in the Internet of Things are different from the cards used in mobile phones. The normal number of mobile phones can be turned on and off every day. The normal erasing of SIM cards is only the switching machine or position replacement. At the time; but in the field of machines, in the field of Internet of Things, its demand changes more, and the number of times of erasing is very high. We have already felt in some industry feedbacks now that the quality of SIM cards in this area is also relatively high. There is also a corresponding speed, its reading, and anomalous exploration. For example, it can be detected at very high temperatures to tell the software inside the SIM card. This includes the impact on the chip, including the impact on the design of the program. There is also a demand for more, the impact of the packaging process, the ordinary SIM card packaging process is using PVC materials, some will not meet the current industrial level requirements. For example, in the case of anti-seismic, in the car, or in extremely harsh environment, the card of the terminal will continuously vibrate, which will lead to some bad contact and strong anti-seismic requirements. There are also specific requirements for temperature, humidity, antistatic and so on. In addition, from a safety point of view, there will be requirements for theft prevention. There have been cases where cards placed on the machine have been stolen and appear in human communication.
Page 1 Page 2 Page 3