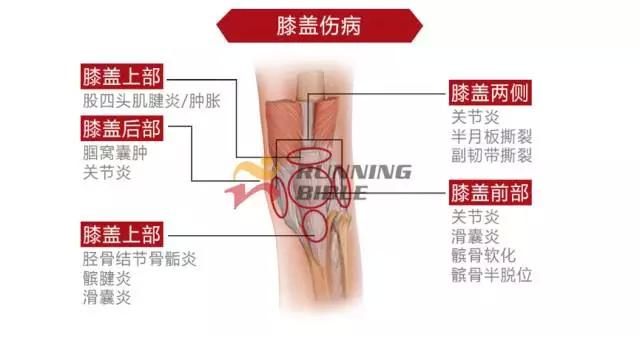
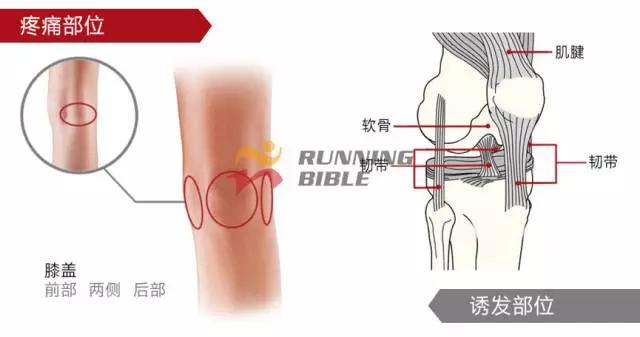
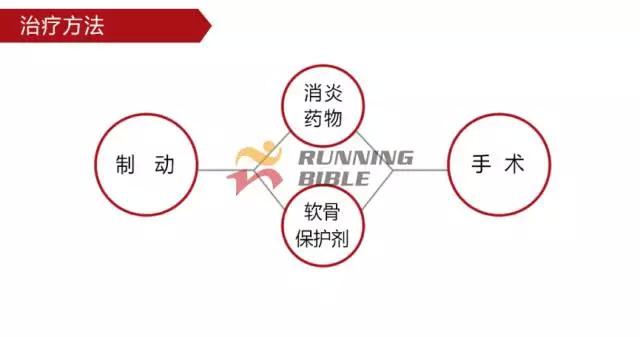
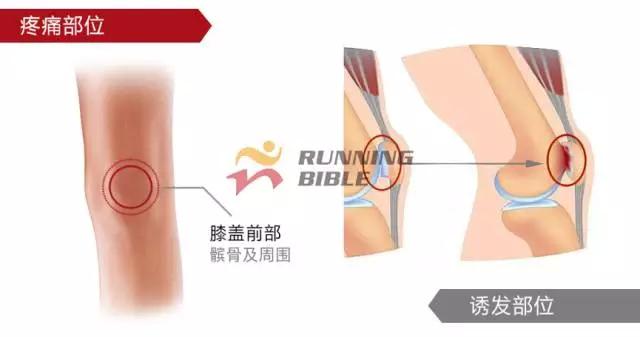
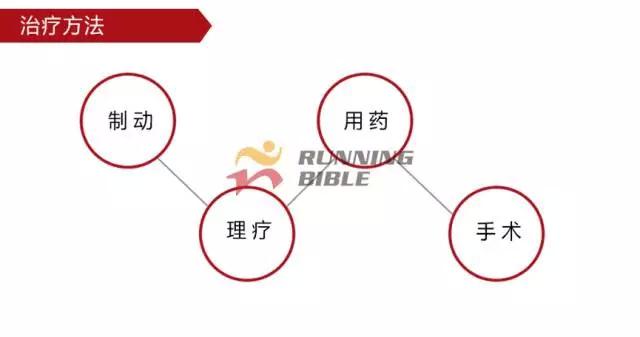
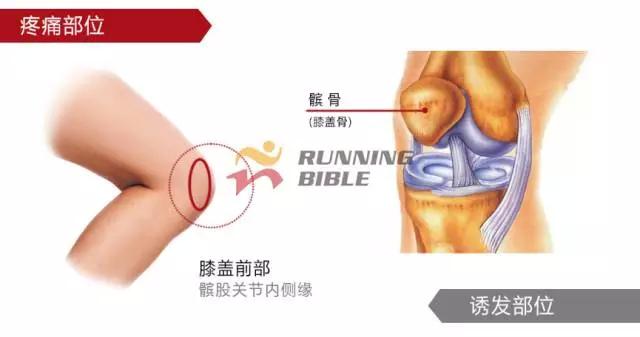
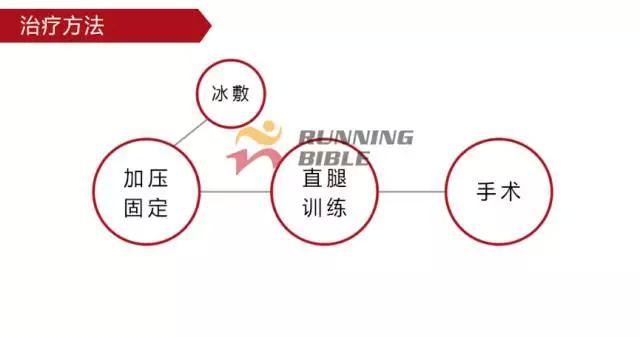
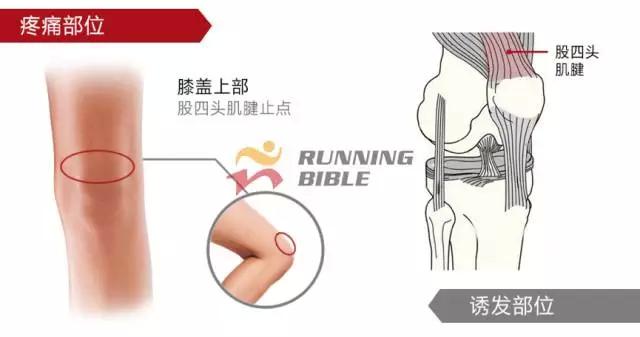
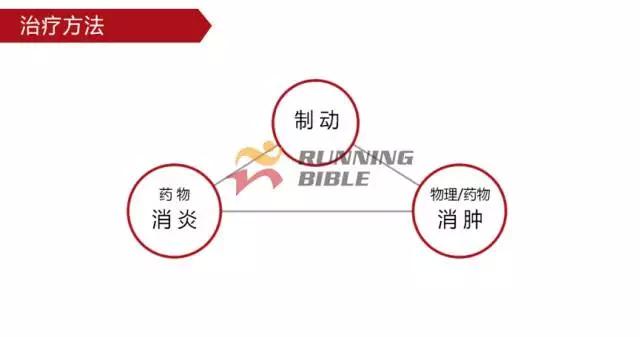
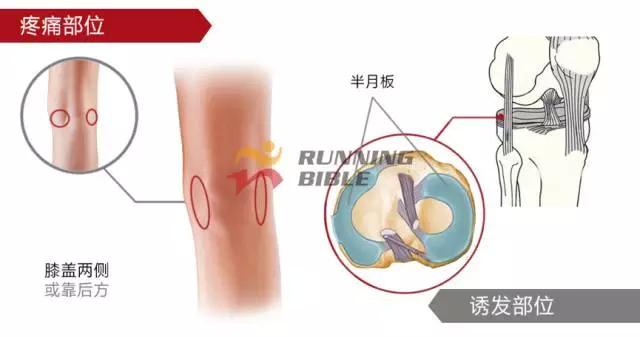
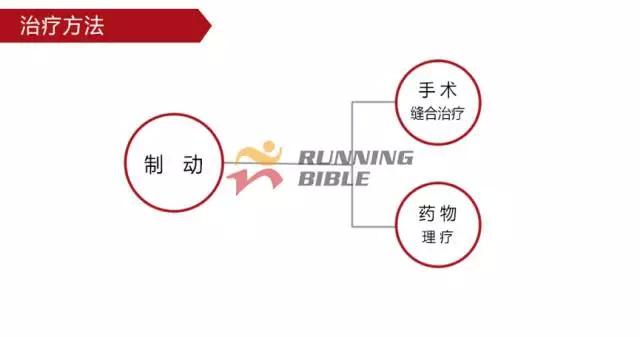
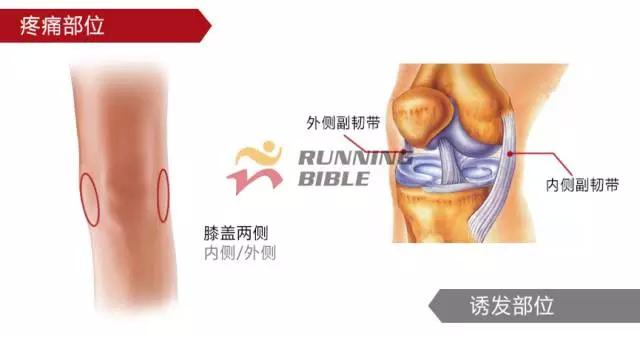
Running to the knee "middle arrow" It’s not an anecdote, it’s not a small thing about sesame mung beans. But, you know? There are many possibilities for knee injuries! 1 Injury 1: Arthritis Pain area: the front of the knee, the left and right sides. Causes of induction: Many knots of hoof tissue are connected between the bones and muscles of the knee. Trauma, excessive local pressure, and excessive strain can cause damage to these tissues and induce inflammation. Clinical manifestations: pain, swelling, fever, motor dysfunction. treatment method: 1Adjust and reduce the amount of training to prevent further wear of soft tissue; 2 take anti-inflammatory drugs under the guidance of a doctor to reduce inflammation; 3 taking a cartilage protective agent such as glucosamine sulfate to promote cartilage growth; 4 The condition is serious and can be treated by surgery. 2 Injury 2: Softening of the tibia Pain area: at the front of the knee, at the tibia (knee bone). Causes of induction: Excessive exercise, rubbing and impact between the sputum strands, causing necrosis of chondrocytes, causing the function of cartilage to take up nutrients in synovial fluid is destroyed, and the tibia is strained. Clinical manifestations: pain in the knee, fatigue, humerus and surrounding edema, hand pressing the tibia in front of the knee joint, there will be dull pain and friction. treatment method: 1 Smaller training volume to avoid direct impact on the movement of the tibia; 2 appropriate amount of painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs; 3 When there is strong pain, apply cold compress, relieve pain after 48h, switch to hot compress, physical therapy; 4 severe cases, surgery is required. 3 Injury 3: humeral subluxation Pain area: the anterior part of the knee and the medial edge of the patellofemoral joint. Causes of induction: When suddenly running or losing balance during running, the inner and outer knees are unbalanced and the humerus is dislocated to the lateral side. Clinical manifestations: sudden pain in the knee joint, dislocation, weakness, and a "squeaky" sound during the activity. treatment method: 1 pressure dressing to fix the knee joint; 2 If there is swelling, ice can be applied every 2~3h; 3 assist in leg contraction training, straight leg raising training, etc.; 4 Severe patients recommend surgery. 4 Injury 4: quadriceps tendon (stop) inflammation Pain area: upper part of the knee, quadriceps of the quadriceps, upper humerus. Causes of induction: a large amount of training in the long term, which causes the quadriceps tendon to be strained and inflamed. Clinical manifestations: tenderness of the upper edge of the humerus, slight swelling, pain, friction, and blockage when bending the knee. treatment method: 1 reduce or avoid knee flexion; 2 partial massage, warm application, promote blood circulation; 3 ice, raise the legs, take anti-tumor drugs, can control the swelling symptoms; 4 take anti-inflammatory drugs. 5 Injury 5: Meniscus tear Pain area: on either side of the knee (on one side), or on the back. Causes of induction: The knees are sprained due to excessive running force and falling, which causes the meniscus to get stuck between the femur and the tibia. Clinical manifestations: walking, squatting is a "squeaky" sound in the knee joint, the joint is suddenly weak or unable to move. treatment method: 1 Stop relevant training to avoid sudden flexion and extension of the knee; 2 surgery (stitching) treatment; 3 medicine physical therapy. 6 Injury 6: collateral ligament tear Pain area: on both sides of the knee. Causes of induction: Unbalanced leg forces during running, leading to knee inversion or eversion, and tearing of one side collateral ligament. Clinical manifestations: motor dysfunction, a large degree of bending, compression will appear pain. treatment method: 1 not completely damaged, need to bring a brace; 2 Complete damage, surgical repair is required. 7 Injury 7: phlegm Pain area: lower part of the knee, below the tibia is connected to the calf tibia. Causes of induction: Improper exercise and excessive training lead to damage and inflammation of the tendon between the tibia and the calf. Clinical manifestations: Pain occurs before and after exercise, or when jumping. treatment method: 1 Adjust the amount of training to avoid strenuous exercise; 2 rest, rest, and appropriate physical therapy; 3 appropriate amount of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory analgesic drugs; 4 If there is a strong pain, local cold compress can be used. 8 Injury 8: Tibia and tuberosity Pain area: lower part of the knee. Causes of induction: Improper or excessive exercise, acute or repeated chronic injury of the tibial tuberosity under the repeated traction of the tendon. Clinical manifestations: Pain in the tibial tuberosity, local swelling, tenderness, red hot symptoms, increased knee pain, knee flexion, and lifting. treatment method: 1 It is recommended to stay still, no need to use medicine, let it heal itself; 2 Avoid running, jumping, squatting, long-distance walking and other sports, limit knee joint activities, and fix with plaster if necessary. 9 Injury 9: bursitis (swollen) Pain area: the front, back and bottom of the knee. Causes of induction: The bursa is a cystic space in the connective tissue. Repeated, long-term, continuous friction and compression caused by overtraining will cause inflammation and swelling of the strain. Clinical manifestations: dysfunction of the activity, local redness, pain or tenderness. treatment method: 1 Stop relevant training and seek medical advice in time; 2 pay attention to cultivation, if necessary, use the splint to fix the knee part; 3 can be injected into the analgesic anti-inflammatory preparation, extracting synovial fluid. Double Desk And Chair,Double School Desk,Double Table Chair,Double School Table AU-PINY FURNITURE CO., LTD , https://www.au-piny.com