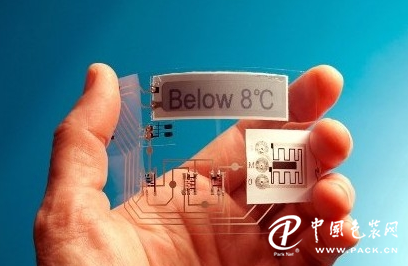
[China Packaging Network] Smart packaging and smart labels are a multi-disciplinary cross-domain application area. It is believed that with the advancement and development of technologies in various fields, smart packaging and labeling will be more widely used and developed. In 1992, the definition of smart packaging was given at the “Smart Packaging†conference held in London. Smart packaging refers to an integrated component or an intrinsic feature (component) in a package, a product, or a product-pack combination. , Through the use of such elements or features, functional components that meet specific requirements are assigned to the functions of the product packaging, or to the use of the product itself. Specifically, smart packaging is the use of new types of packaging materials, structures and forms of active intervention and protection of the quality of goods and security of circulation; the use of information collection, management, control and processing technology to complete the optimal management of transport packaging systems. Classified according to the working principle, smart packaging can be divided into functional material type intelligent packaging, functional structure type intelligent packaging and information type intelligent packaging. Functional material type smart packaging refers to the use of new smart packaging materials to increase and enhance packaging functions to achieve specific packaging purposes. For example, through the use of photoelectric, humidity-sensitive, temperature-sensitive, gas-sensitive, and other functional materials, the packaging that has "identification" and "judgment" functions for environmental factors is a typical material-based intelligent packaging. Classified according to the application areas, smart packaging can be divided into: intelligent food packaging, pharmaceutical intelligent packaging, cosmetics, smart packaging. Smart labels are a new technology that emerged in the 1990s and are widely used in the fields of food storage, transportation and sales. The use of smart labels facilitates the promotion of brands, increases interest, entertainment, novelty, and easily attracts the attention of consumers, improves differences, and is more easily accepted by consumers. There are mainly two kinds of smart labels, one is a label with diagnostic or detection functions, which mainly includes a time-temperature indication label, a freshness indication label, an oxygen indicating label, a carbon dioxide indicating label, a package leakage label, a pathogenic indicator label, and the like; The other is the use of information technology labels, including radio frequency identification (RFID) tags, electronic surveillance tags, electromagnetic identification tags. Time-temperature indicator Time-Temperature Indication Labels (TTIs) are generally based on time and temperature cumulative chemical change effects such as polymerization reactions, photochromic reactions, oxidation reactions, etc.; or based on cumulative biological changes such as enzyme reactions, lactic acid reactions, etc.; or based on Physical characteristics, process-induced changes, such as diffusion, thermochromism, photoacoustic lattice changes, etc. Using the above principles or changes to produce irreversible changes shows the cumulative effects of time and temperature. Time-temperature indication labels are often used in food packaging. The Checkpoint® TTI label (see Figure 1) is based on the enzyme decomposing the fatty substrate on the label at a higher temperature, causing the pH of the substrate to decrease, discoloring the indicator. The PakSense® TTI label (see Figure 2) can simultaneously indicate the temperatures and times experienced during food storage and retailing. If the storage temperature exceeds a set point, it is visually recorded in a graphically similar manner. The 3M Monitor MarkTM TTI label (see Figure 3) can display the accumulated time when the ambient temperature of the food is above a certain set value, which is recorded according to the irreversible change of the color of the dye. The dye on the label starts to look white. When the exposure temperature exceeds the preset temperature limit of the label, the solid ester dye melts and starts to move to the right along the wetting channel. The first observation window on the left side begins to turn blue. As time-temperature changes, the dye gradually moves to the right until the end of the circular observation window. Humidity display label The humidity display label reflects the humidity in the packaging environment where the product is located through the change in its own color, and is widely used in the packaging of optical equipment, instrumentation, electronic components, and sensitive components. The humidity display label can facilitate the user to quickly determine the humidity in the product package through the color change of the label. If the humidity in the package reaches or exceeds the critical humidity value, the corresponding indicator dot on the humidity display label will gradually change from blue to blue. Pink. This color change is reversible, and the dots gradually change from pink to blue under low humidity conditions. The humidity label is an environmental measurement tool that can easily detect whether the relative humidity in the sealed package is safe. Packaging integrity indicator Many foods use modified atmosphere packaging to extend the shelf life of the product. When the air enters the modified atmosphere packaging, it may lead to increased activity of harmful bacteria, making the food dark in color, and may even produce an unpleasant odor and lose its nutritional value. UPM developed a package integrity indicator (see Figure 4) to monitor whether the modified atmosphere package is damaged and complete. The integrity of the modified atmosphere packaging is indicated by monitoring the ratio of CO2, N2, and O2 in the package. Freshness indicator The Freshness Indicator Label directly indicates microbial status in the food by reacting to the metabolism of the microorganism during growth. Bacteria breeding markers indicate the number of pathogenic bacteria. The response principle can be to react with certain metabolites (volatiles or non-volatiles), or to establish a pathogen detection system based on the principle of immunochemical reaction, or pH dyes to detect the deterioration of foods. Volatile biogenic amines, to show freshness (threshold). The freshness indicator (see Figure 5) developed by Mitsubishi of Japan is realized by detecting the oxygen content in the package. For oxygen-absorbing packaging, if the oxygen-absorbing capacity of the material has disappeared, the oxygen concentration in the headspace of the package will increase, and the indicator of the ability to absorb (oxygen) will change color. When the oxygen concentration in the package is <0.1%, the label is light pink, indicating that there is no oxygen in the package and the oxygen absorber is active; when the oxygen concentration in the package is >0.5%, the label will turn blue. Anti-counterfeiting DNA tags Anti-counterfeit DNA tags are randomly cut from the DNA sequence of the product, and special inks are printed on the surface of the tags through special methods. When using electronic equipment for scanning, the corresponding DNA sequence can be seen to verify the authenticity of the product. RFID tags RFID tags use radio frequency identification technology to achieve the functions of target recognition, item tracking, and information collection through the interaction with readers, data exchange, and management systems. Through RFID tags, food can be traced back to the source, and at the same time, the storage temperature and maturity of the food can be grasped at any time. For temperature-sensitive monitoring of red wine storage and transportation environment, RFID active labels can be used to record time-ambient temperatures, as well as origin, storage environment, and wine information identification and product quality traceability. Anti-pour label If the product is tilted at an angle of more than 45°, a device in the anti-tip label changes and the indicator window changes from white to red. When the display window of the anti-drop label is in a red state, the display window of the monitor cannot be changed, so that it can become a permanent proof of dumping. Anti-dumping labels can remind transportation personnel to take extra care when handling goods, effectively prevent and reduce the risk of damage to the goods during transit, and enable the perpetrators to take responsibility for their responsibility. Collision display label When the external force of the collision display label exceeds its setting range, the middle crystal tube will turn from white to red. It is applicable to the entire process of transportation, such as photographic equipment, cameras and other digital products, as well as various types of instrumentation, communication equipment, medical supplies and equipment, military equipment, and aviation equipment. Intelligent packaging and smart labels are a cross-disciplinary application field. It is believed that with the advancement and development of technologies in various fields, smart packaging and labels will be more widely used and developed. essential oil Jiangsu Raymeel Home Decoration Co., Ltd. , https://www.raymeelhome.com